Dental implants have revolutionized the field of dentistry, providing millions of people with a permanent solution for missing teeth. Over the years, implant surgical guides have evolved from primitive to sophisticated tools. This transformation has been made possible due to advancements in technology, which have significantly improved the process of dental implantation. In this article, we will take a closer look at the history of implant surgical guides and discuss how they have evolved over time.
A Brief History of Implant Surgical Guides
Implant surgical guides, or surgical stents, have played a crucial role in dental implant procedures since their inception. These tools help ensure the accurate placement of dental implants in the patient’s jawbone. Initially, dental practitioners had to rely on their experience and skill to place the implant without any guidance. This method was prone to errors and complications, as it heavily relied on the surgeon’s expertise and dexterity.
With the advancements in technology, implant surgical guides became more accurate and reliable, leading to more predictable and successful outcomes. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) technology were introduced to create more accurate surgical guides, enabling dentists to plan the implant placement with greater precision.
The Evolution of Implant Surgical Guides
As technology progressed, various types of surgical guides for dental implants were developed to enhance the accuracy and predictability of the implant placement process. One of the most significant innovations in this field is 3D guided dental implants.
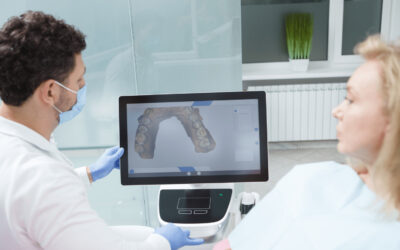
3D guided dental implants use advanced imaging techniques, such as cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), to create a detailed three-dimensional model of the patient’s jawbone. This model allows dentists to plan the exact position, angle, and depth of the dental implant before surgery. The surgical guide, or dental implant stent, is then fabricated using CAD/CAM technology, ensuring a precise fit during the procedure.
3D guided dental implants have several advantages over traditional methods, such as reduced surgery time, less invasive procedures, and improved patient comfort. This technology enables dentists to perform complex dental implant procedures with higher accuracy, reducing the risk of complications and improving the overall success rate.
Changing the Implant Surgical Guides World!
The evolution of implant surgical guides has significantly improved the field of dental implantology. Modern implant surgical guides, such as those used in 3D guided dental implants, offer numerous benefits compared to their earlier counterparts. They provide a more accurate, predictable, and efficient method for dental implant placement, leading to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction.
The advancements in implant surgical guide technology have revolutionized dental implant procedures, making them more precise, reliable, and comfortable for patients. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in this field, ensuring that dental implants remain the gold standard for tooth replacement.
Questions or concerns? Please feel free to contact ConeScan to learn more!
3D guided dental implants FAQ
What are the different types of implant surgical guide?
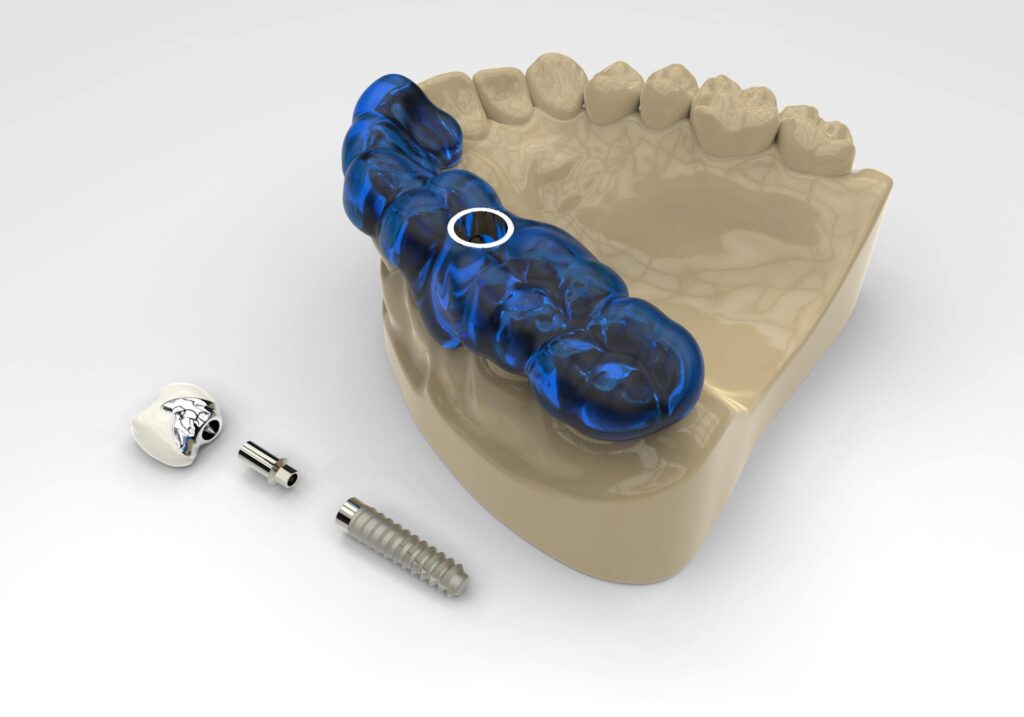
There are several types of implant surgical guides, including tooth-supported, mucosa-supported, and bone-supported guides. The choice of guide depends on the specific clinical situation and dentist’s preference.
Why would a dentist use a surgical stent during implant surgery?
A dentist would use a dental surgical stent to ensure accurate and precise placement of the implant, minimize risks and complications, and improve the overall predictability of the procedure.
What is a guide stent for implant placement?
A guide stent for implant placement, also known as an implant surgical guide or dental implant stent, is a custom-made device that assists the dentist in accurately positioning the dental implant within the patient’s jawbone during surgery.